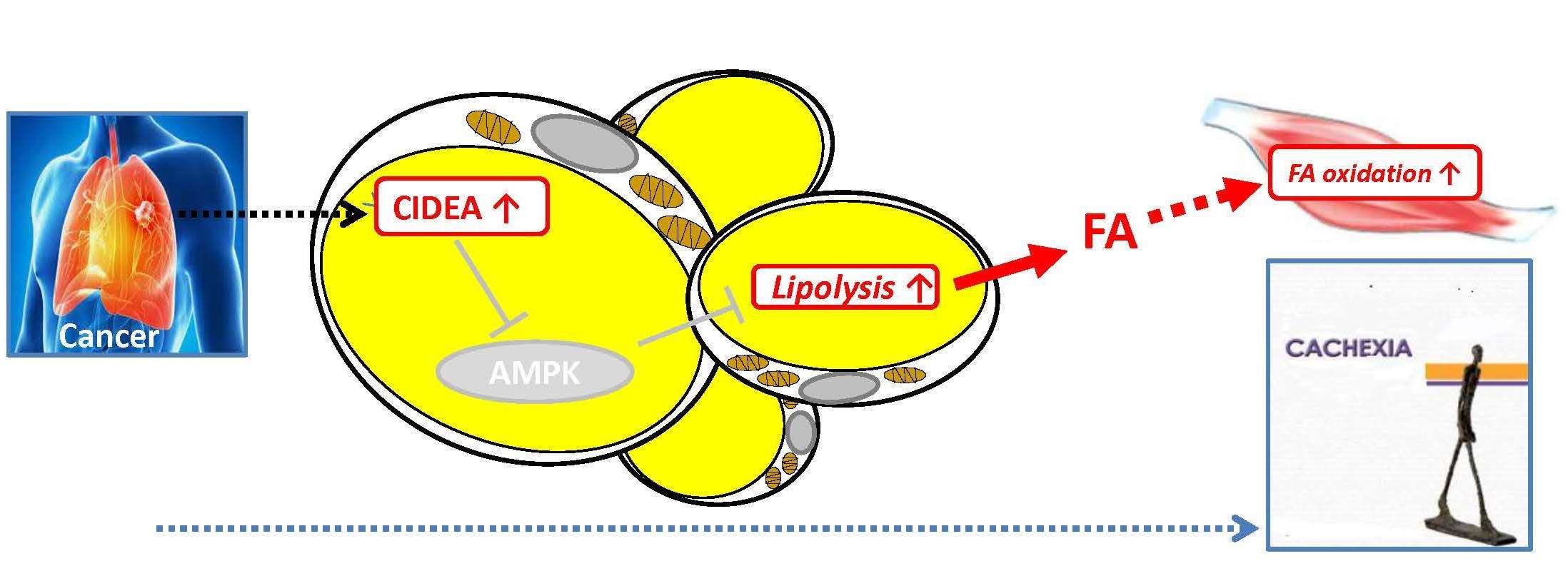
Cancer cachexia can reflect aberrant metabolism of adipose tissue
A large part of patients with malignant disease suffer also from cachexia, i.e. a significant body weight loss, which cannot be reversed by dietary measures.
Cachexia is initiated by a loss of adipose tissue, which is followed by wasting of skeletal muscle. Cachexia worsens prognosis of patient’s survival. Until recently, it was supposed that cachexia develops in response to deprivation of host energy resources by growing cancer. However, contemporary research indicates that cachexia may result from the integrative global metabolic response to tumor. The new study shows that the loss of adipose tissue during cachexia could be caused by „aberrant regulation“ of metabolism of adipose tissue itself. Tumor-released factor(s), the nature of which isn’t known, could negatively influence activity of the regulatory enzyme AMPK through the factor CIDEA, leading to augmented triglyceride lipolysis in adipocytes and to excessive release of fatty acids from adipose tissue. This results in adipose tissue loss, while fatty acids are „burned“ in skeletal muscle and other tissues. Cachexia in mice was counteracted by normalizing the activity of AMPK in adipocytes. These results indicate that treatment of patients with cachexia should also target adipose tissue metabolism itself. Scientists from 13 institutes located in 7 different countries, also including the scientists at the Institute of Physiology CAS, participated in this study, which was largely funded by a grant from the European Union (http://www.diabat.org/content/index_eng.html).
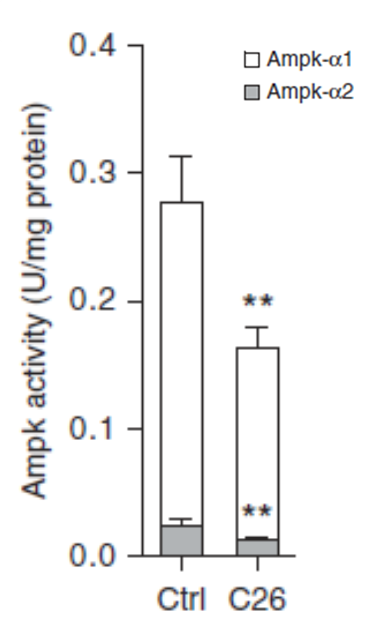
Inhibition of AMPK activity in adipose tissue of mice in response to a tumor; Ctrl: control tissue, C26: tissue with a tumor (assessed at the Institute of Physiology CAS).
Rohm, M. - Schäfer, M. - Laurent, V. - Üstünel, B. E. - Niopek, K. - Algire, C. - Hautzinger, O. - Sijmonsma, T. P. - Zota, A. - Medrikova, D. - Pellegata, N. S. - Ryden, M. - Kulyte, A. - Dahlman, I. - Arner, P. - Petrovic, N. - Cannon, B. - Amri, E. Z. - Kemp, B. E. - Steinberg, G. R. - Janovská, Petra - Kopecký, Jan - Wolfrun, Ch. - Blüher, M. - Diaz, M. B. - Herzig, S. An AMP-activated protein kinase–stabilizing peptide ameliorates adipose tissue wasting in cancer cachexia in mice. Nature Medicine. Roč. 22, č. 10 (2016), s. 1120-1130 ISSN 1078-8956. IF: 30.357.
