Neurosteroids and steroid hormones are allosteric modulators of muscarinic receptors

Dolejší, E.; Szánti-Pintér, E.; Chetverikov, N.; Nelic, D.; Randáková, A.; Doležal, V.; Kudová, E.; Jakubík, J. Neurosteroids and Steroid Hormones Are Allosteric Modulators of Muscarinic Receptors. Neuropharmacology 2021, 199, 108798, doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2021.108798.
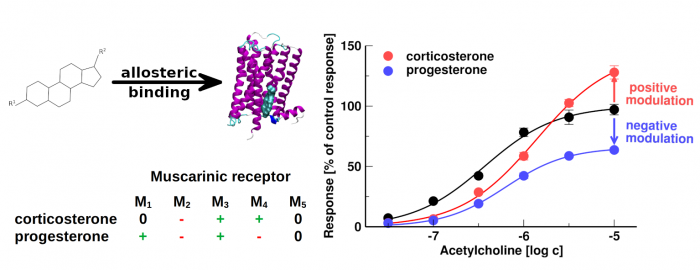
- Some neurosteroids and steroid hormones bind to muscarinic acetylcholine receptors with the affinity of 100 nM or greater
- Steroids acting at nanomolar concentrations represent the novel pharmacophore of allosteric modulators of muscarinic receptors
- Corticosterone and progesterone allosterically modulate muscarinic receptors at physiologically relevant concentrations
The membrane cholesterol was found to bind and modulate the function of several G-protein coupled receptors including muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. We investigated the binding of 20 steroidal compounds including neurosteroids and steroid hormones to muscarinic receptors. Corticosterone, progesterone and some neuro- steroids bound to muscarinic receptors with the affinity of 100 nM or greater. We show that corticosterone and progesterone allosterically modulate the functional response of muscarinic receptors to acetylcholine at physiologically relevant concentrations. It can play a role in stress control or in pregnancy, conditions where levels of these hormones dramatically oscillate. Allosteric modulation of muscarinic receptors via the cholesterol- binding site represents a new pharmacological approach to diseases associated with altered cholinergic signalling. Further, we established a structure-activity relationship for steroid-based allosteric modulators of muscarinic receptors.
