Neurosteroid pregnenolone sulfate - revealing of its site of action at the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor
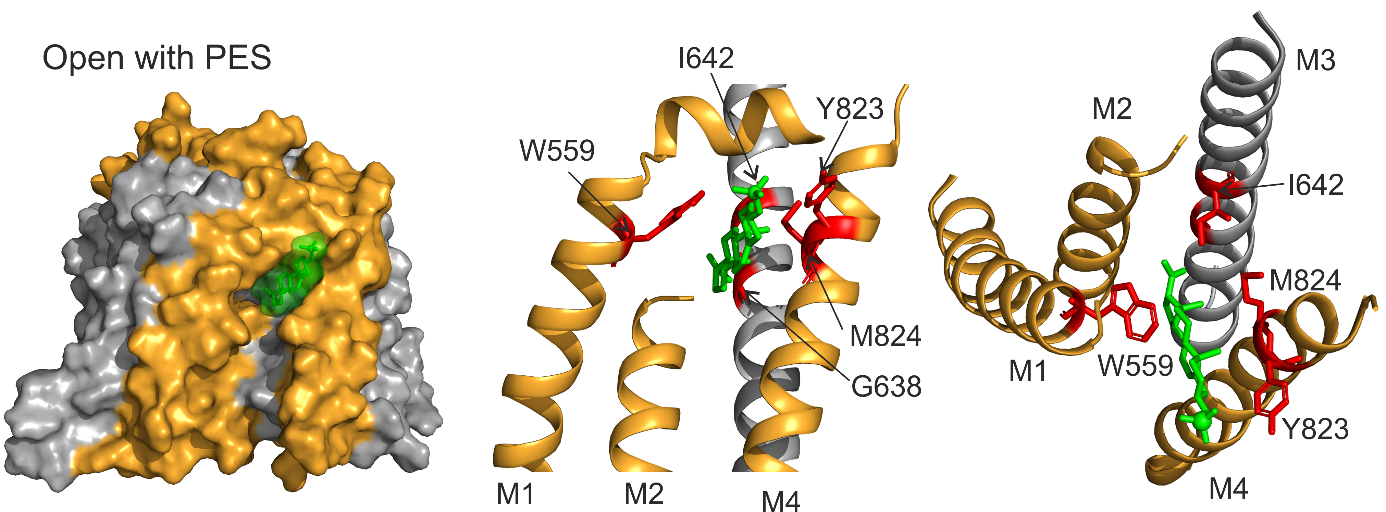
NMDA receptors are ion channels involved in the transmission of electrical signals between nerve cells. Their insufficient function contributes to severe neuropsychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia or autism. NMDA receptor activity can be increased by a variety of compounds, including neurosteroids. In collaboration with the Institute of Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry CAS, we identified the binding site and elucidated the mechanism of action of the naturally occurring neurosteroid pregnenolone sulfate (PES). PES binds to the interface of membrane domains of the NMDA receptor in the closed state, and subsequent activation of the receptor by glutamate leads to a rearrangement of the membrane domains and stabilization of the open state of the NMDA receptor ion channel. These findings may contribute to the development of new drugs for the treatment of diseases associated with the dysfunction of the glutamatergic system.
The interaction of the PES molecule (green) with the membrane domains of the NMDA receptor in the open state was obtained by docking followed by molecular dynamics simulation. Amino acids involved in the interaction with the PES molecule are highlighted in red.
Hrčka Krausová B, Kysilov B, Černý J, Vyklický V, Smejkalová T, Ladislav M, Balík A, Kořínek M, Chodounská H, Kudová E, Vyklický ml. L. Site of Action of Brain Neurosteroid Pregnenolone Sulfate at the N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor. Journal of Neuroscience. 2020; 40 (31) 5922-5936. IF: 5.673 DOI
